Roof Framing Plans | Basics, Definition, Roof Framing & Roof Truss
Articles, products, and services offered on this site are for informational purposes only. We are part of the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program. Amazon.com is compensated for sales resulting from links on our website.
Please review our disclaimer before acting based on anything you read or see.
Many homeowners assume that the art of roof framing is a reasonably easy trade for a builder to learn. However, if you don’t have the roof framing plans very hardly anything can be done. The task is very complex. The necessary resources must be available to make accurate cuts in the framing material, one of the most critical aspects of the entire framing process.
Read More: How To Cut Colorbond Roofing Sheets
As much as your idea is to make simple roofs, the importance of a properly designed top provides the strength and balance needed for the entire structure.
Related knowledge and having the right skills are essential elements when building this structure to properly transfer the gravitational pull, uplift, and lateral load to the main foundation of the house.
Since making the proper cuts in this roofing system is vital to the building’s overall structure, all builders must learn. The importance of making cuts in the correct part of the structure’s material when performing any major repair or planning a complete renovation or replacement of this roofing system should be known before the project begins.
Learn More: Weight Of Roofing Materials
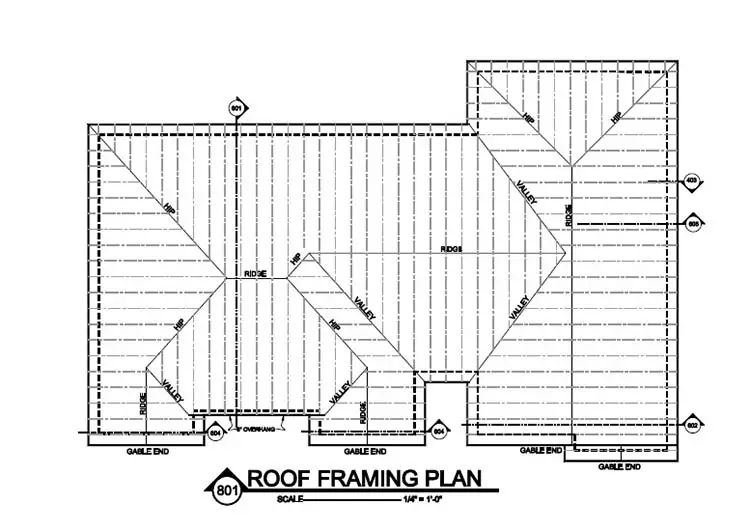
One of the essential parts of resilient roof construction is the initial plan for the roof framing plan. Roof framing describes how a group of rafters is placed or joined together to support the roof deck. To framing the roof correctly, it is vital to understand your roof’s unique shape and dimensions because they significantly impact the geometry of the roof reinforcement.
What is a Roof Framing Plan?

A roof framing plan is the representation of a structure’s or building’s frame components. The main objective of this plan is to help both contractor and manufacturer take accurate measurements and determine construction feasibility and material requirements for construction projects. Typically, a roof framing plan shows up in residential construction plans rather than commercial or industrial-scale projects.
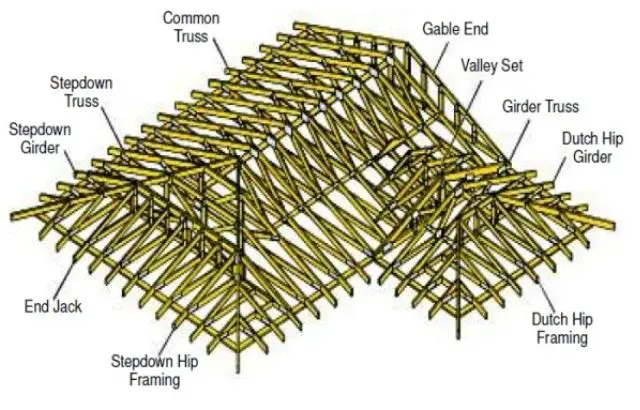
The most common use of a roof framing plan refers to the basic structural definition that supports any given building’s overall framework for large room space such as attics, basements, garages, kitchens, bedrooms, and lounges. Such structures are supported by multiple beams called trusses which are either angled diagonally from one another or placed parallel with each other spaced an appropriate distance from one another. The space between these trusses is then covered with plywood sheets. In some cases, OSB sheets support the roof’s weight, protected by shingles on top of the plywood. Roof framing plans show how the trusses will be placed together and indicate where a component such as a wall will connect to them and at what angle it should slope off when it does so.
Types of Roofs
When building roof framing plans, a lot of things to think about
There are two fundamental types of roof structures in the roofing industry:
- Pole framing
- Lattice framing
Each of these uses a fundamentally different approach to constructing the roof framing. For this purpose, almost always ordinary lumber is required, and the structure is built one beam at a time.
In the case of the truss frame, you will use prefabricated triangular-shaped pieces of wood to build the roof frame. You have to decide whether to follow the classic framing method, which requires more work or if you prefer to use the newer one from the beginning.
Read More: Best Plywood For Roofs
Less Labour-Intensive Truss Framing Process
Choosing the suitable framing for your roof
- If you look at the different houses in your locality, you will probably discover a wide variety of roof shapes.
- The most famous roofs are gable, hipped, gambrel, and floor plan.
- Gambrel roof framing plans are often beneficial.
- You can also find a mix of two or even more roof styles, such as a hipped roof with a gable dormer.
- As you can probably guess, every type of roof needs a different structure.
Generally speaking, the simpler the type of roof, the easier it will be to build a roof frame to support it.
However, even a relatively common roof type, such as a gable roof, can be made more complex using overhangs, hips, and dormers. Though, when thinking from a geometric perspective, the reason for this problem becomes apparent.
Every little twist or variation on a familiar triangle shape (i.e., the standard gable roof shape) will require additional calculation and prep work before building the frame.
A bold statement arises from this. Lattice framing is only appropriate for gable and hipped roof types; for all other roof types, you should use the stick framing approach. This is because the truss framing approach is based on prefabricated, pre-cut shapes that may or may not fit the actual dimensions of your roof.
If you plan to make additions or modifications to your roof later, it is preferable to use the stick framing approach.
Calculation Needed for the Roof Structure
As noted above, roof framing is really about getting the geometry of your roof correct.
Therefore, it is crucial to understand how each of the following calculations will affect the roof framing process. At this point, even a superficial level can make a difference.
Read More: Can You Paint A Metal Roof
- Lapse
- Rise
- Run
- Line Length
- Playing Field
Let us study all these terms within the concept of the classic gable roof. Span refers to the accurate measurements at the top of your building, from one exterior wall to the other outer wall. Once you know the span, you can calculate the rise. The rise is the accurate measurement from the center point of the span to the top of the roof. In the case of a gable roof, this will be the “sharp point” where two sides of the roof meet.
You can then calculate the run, which is half the span measurement.
In the case of thinking in geometry and triangles, as it is logical when dealing with a roof structure work, then the length of the line is simply the hypotenuse of the triangle defined by the rise and run.
You can measure it from the outside wall where the run ends to the top of the elevation.
The final calculation, the slope, can be understood as the angle in degrees or slope the roof has.
Mathematically, it is simply “rise overrun,” which tells you exactly how high a roof rises per unit of run.
Within the field of roofing, there is a tradition of expressing the “height over the course” in the form of 12. This figure corresponds to 12 inches or 1 foot. This 12 conforms to 12 inches or 1 foot. Therefore, if a slope is 4/12, it means that the roof rises 4 inches for every 12 inches of span.
The slope can be shallow or steep, depending on the needs of the roof. For example, in areas where snowfall is abundant, it makes sense to create a steeper slope to facilitate snow removal. However, you can find a roof framing calculator to help you with this procedure on the internet.
Measure and cut the framing joists
In the stick frame technique, it will be necessary to invest some time in measuring and cutting the beams according to the calculations.
Various procedures can be applied for this purpose, but the most popular way uses the traditional framing square.
Using the traditional framing square and the above calculations, you can place the joists properly.

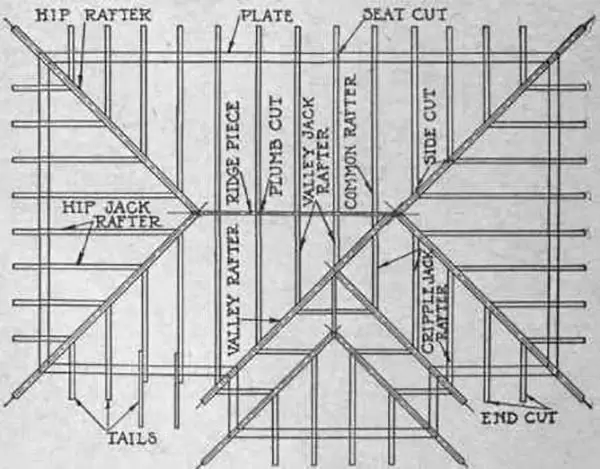
In terms of cutting the joists, there are three basic types of cuts you need to know:
- Plumb cut
- Bird’s mouth cut
- Tail cut
These cuts determine how two different pieces of wood will interlock and fit together to form a strong frame.
Conclusions about the Roof Structure
Therefore, the initial roof construction project has to include several features, such as roof shape and relevant community building codes. All of these are important for an excellent structural roof framing plan.
Next, you will need to choose between two very different types of roof framing (stick framing or truss framing). Once you’ve done that, it’s time to do all the precise calculations to make the wood pieces fit together correctly. The goal, of course, is that all parts of the roof frame fit together perfectly to provide the perfect support for the new roof.
Precise Cutting Considerations
To achieve an accurate cut, master carpenters calculate two vital dimensions. The overall rise of total vertical height dimension from the midpoint of the rafter plate to the ridge and the general run is half the building’s width). These two key terms are the essential elements to ensure the correct cut and pitch before roof construction.
Besides, carpenters always consider the type of loads and the allowable span of the building, as these directly impact the kind of wood to be used, the correct spacing, and the dimension of the beams.
Generally, the magnitude of the width varies depending on the wind pressure and the amount of snowfall expected in a given region.
Often, there are specific building codes in the regions that regulate the allowable span for the structure.
The designs used in cutting roofs also depend on the attic, material, and additional features such as skylights or valleys and other dormers. As a result, the various cuts are pretty tricky. In the case of heavier material, the roof design must be strong enough to support the weight. Framing or cutting roofs require a great deal of skill and knowledge in the science of carpentry.
This subject is very different from other construction tasks, as many factors must be taken into account to ensure that proper construction takes place.
Each cut must be precise. The degree of slope must be calculated correctly. The external elements must be recognized, and the overall roof design must be analyzed so that the result is free of errors. In roof design, it is essential to focus on proper framing during the construction phase. The top of a house is as necessary as its foundation to avoid future failure or collapse.
Roof Framing Plans: FAQs
What are the critical elements in the roof framing plan?
The framing system includes load-bearing walls, trusses, rafters, posts, and attic floor framing. All of these components are critical to support a lateral load.
What are the different types of roof framing members?
A basic conventional roof consists of rafters, roof trusses, and a ridge board. The most sophisticated roofs contain several elements, such as suspenders, valley beams, and jack rafters.
How do I estimate roof framing?
Determine the span: For this, the total width of the building where the beams will be placed must be measured.
Determine the run: You must divide this distance by exactly half. For example, 24 feet separated by 2 = 12 feet of run.
What are the three main basic parts of a roof framing plan?
The roof of your house is a remarkable architectural feat. The rafters are the horizontal beams that support the ceiling joists, which hold up an even more important element – the ridge board. But what’s incredible about roofs isn’t just their ability to keep water out and make sure no one gets wet when it rains; they also have so many different types!
There are gable roofs, hipped roofs, gambrel roofs (did you know those were called “gingerbread” houses?). Mansard-style buildings with steeply sloping sides of any type imaginable can be found on top of some building somewhere around town or across the country if you look hard enough.
What are 2 types of roof framing members?
Premanufactured trusses are generally seen as a more cost-effective option when constructing the roof of your house, but stick framing is often chosen because it’s considered to be sturdier.
Since you’re trying to build one of these things, there are two ways that people typically go about doing this: with premanufactured trusses or rafters and ceiling joists (commonly called “stick” construction). Some may say that using prefabricated pieces can save you money on labor costs–but others maintain their opinion that stick framing makes for stronger roofs in the long run.
Are trusses cheaper than rafters?
Trusses are an engineer’s way of saying, “I have a solution to your problem.” They’re quick and easy. In contrast, rafters take longer because they must be built offsite then laboriously installed onto the roof by hand. Trusses can be assembled in as little as one day in some cases due to their pre-made design, which is made possible by automation like computer-driven saws.
How is the roof plan different from the roof framing plan?
A roof framing plan is as unique to the building design and construction process as a fingerprint. However, a common misconception about these plans is they are just blueprints for roofs. But rather than show you how your house will look from outside or inside on top of its walls. This shows what makes up the “bones” of your home. The basic structure goes all around and through each level in an X-shape pattern with posts holding beams that then support joists (the floorboards) where ceilings connect them.
Conclusion
The elaboration of a roof is a subject that could become a little delicate. This is because it must be perfectly structured. It is very precise to have the steel roof framing plan details.
All this allows your roof to last for many years and not fall apart in a short time.
The screen scale and the scale in the diagram are significant since the whole job depends in part on them. The use of scale template images is also crucial in this process.


Comments are closed.