The nitrogen cycle is a fundamental process in nature, playing a crucial role in ecosystems’ overall health and balance. It involves the conversion of nitrogen compounds from one form to another, ensuring that plants and animals have access to this essential nutrient.
However, fertilizer use can have positive and negative effects on the nitrogen cycle, which in turn impacts the environment. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the nitrogen cycle and understand how fertilizer usage can influence this delicate balance.
What is the Nitrogen Cycle
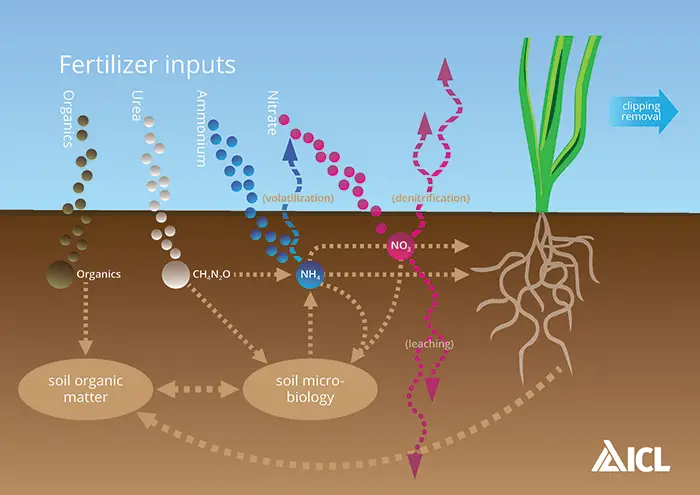
The nitrogen cycle is a complex and interconnected process involving transforming nitrogen in different forms. Nitrogen is an essential element required for the growth and development of living organisms, including plants and animals. However, most organisms do not directly use the atmospheric nitrogen gas (N2) that makes up about 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It must be converted into other forms, such as ammonia (NH3) or nitrate (NO3-), through biological and chemical reactions.
The nitrogen cycle consists of several stages, including nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification. During nitrogen fixation, certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which plants can use.
Nitrification involves the conversion of ammonia into nitrate by other bacteria. Assimilation occurs when plants take up nitrate and incorporate it into their tissues. Ammonification breaks down organic nitrogen compounds into ammonia, while denitrification converts nitrate into atmospheric nitrogen gas.
The Positive Effects of Fertilizers on Plant Growth
Fertilizer plays a vital role in promoting plant growth and improving crop yields. Here are five tips to understand the positive effects of fertilizer on plants:
Increased Nutrient Availability
Fertilizers provide plants with readily available nutrients, ensuring an adequate supply for optimal growth and development. This is especially important in soils with low nutrient levels.
Improved Root Development
Fertilizer stimulates root growth, allowing plants to absorb water and nutrients more efficiently. This leads to stronger, healthier plants better equipped to withstand environmental stressors.
Balanced Nutrient Uptake
Fertilizer formulations are carefully designed to provide a balanced mix of essential nutrients. This ensures that plants receive all the necessary elements in proportions, promoting overall plant health.
Increased Crop Yields
By supplying plants with the nutrients they need, fertilizer can significantly increase crop yields. This is particularly important in modern agriculture, where high yields are essential to meet the growing demand for food.
How Does the Use of Fertilizer Affect the Nitrogen Cycle?
The use of fertilizer can have a significant impact on the nitrogen cycle. When fertilizers are applied, they introduce additional nitrogen compounds into the soil. This can disrupt the natural balance of nitrogen in the ecosystem and alter the rates of nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification.
Excessive use of fertilizers can lead to an increase in nitrate levels in the soil and water bodies. This excess nitrate can be converted into nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Additionally, introducing excess nitrogen can lead to imbalances in nutrient availability, affecting plant and microbial communities.
Using fertilizers judiciously and following recommended application rates and timing is crucial. This helps to minimize the negative impacts on the nitrogen cycle and maintain a healthy balance in the ecosystem.
Alternative Methods to Traditional Fertilizers
In addition to sustainable fertilizer practices, alternative methods to traditional fertilizers can also be employed to reduce the impact on the nitrogen cycle. Here are some alternative options to consider:
Biofertilizers
Biofertilizers contain beneficial microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability and stimulate plant growth. They can be used with traditional fertilizers to reduce the overall fertilizer requirements.
Crop Residues and Cover Crops
Instead of removing crop residues, leaving them on the field can contribute to soil organic matter and nutrient availability for subsequent crops. Cover crops can also be grown during fallow periods to provide additional nutrients and improve soil structure.
My Opinion
The use of fertilizer undoubtedly has a profound impact on the nitrogen cycle and, consequently, the environment. While fertilizer is vital in promoting plant growth and increasing crop yields, its excessive use can disrupt the delicate balance of the nitrogen cycle, leading to negative consequences such as nutrient pollution, eutrophication, and air pollution.
Adopting sustainable fertilizer practices, such as precision agriculture, controlled-release fertilizers, and nutrient cycling, is essential to mitigate the impact on the nitrogen cycle. Additionally, exploring alternative methods to traditional fertilizers, such as organic fertilizers and biofertilizers, can reduce reliance on synthetic fertilizers and minimize their environmental footprint.